+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Lassen Sie die Welt von Verbundwerkstoffen profitieren!
Fiberglass Prepreg: The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Composites
Introduction
Fiberglass prepreg has become a cornerstone in high-performance composite manufacturing, offering unparalleled strength, consistency, and efficiency. From aerospace to automotive and marine industries, prepreg fiberglass provides superior mechanical properties, reduced material waste, and precise control over resin distribution. Unlike traditional wet layup methods, which involve manually applying resin to dry fabric, fiberglass prepreg comes pre-impregnated with a resin system that remains dormant until heat and pressure activate the curing process.
This guide provides an in-depth look at fiberglass prepreg, including its composition, manufacturing process, advantages, applications, curing techniques, storage considerations, challenges, and future trends. Whether you’re an engineer, manufacturer, or DIY enthusiast, understanding prepreg fiberglass will help you make informed decisions for high-performance composite applications.

What is Fiberglass Prepreg?
Definition and Composition
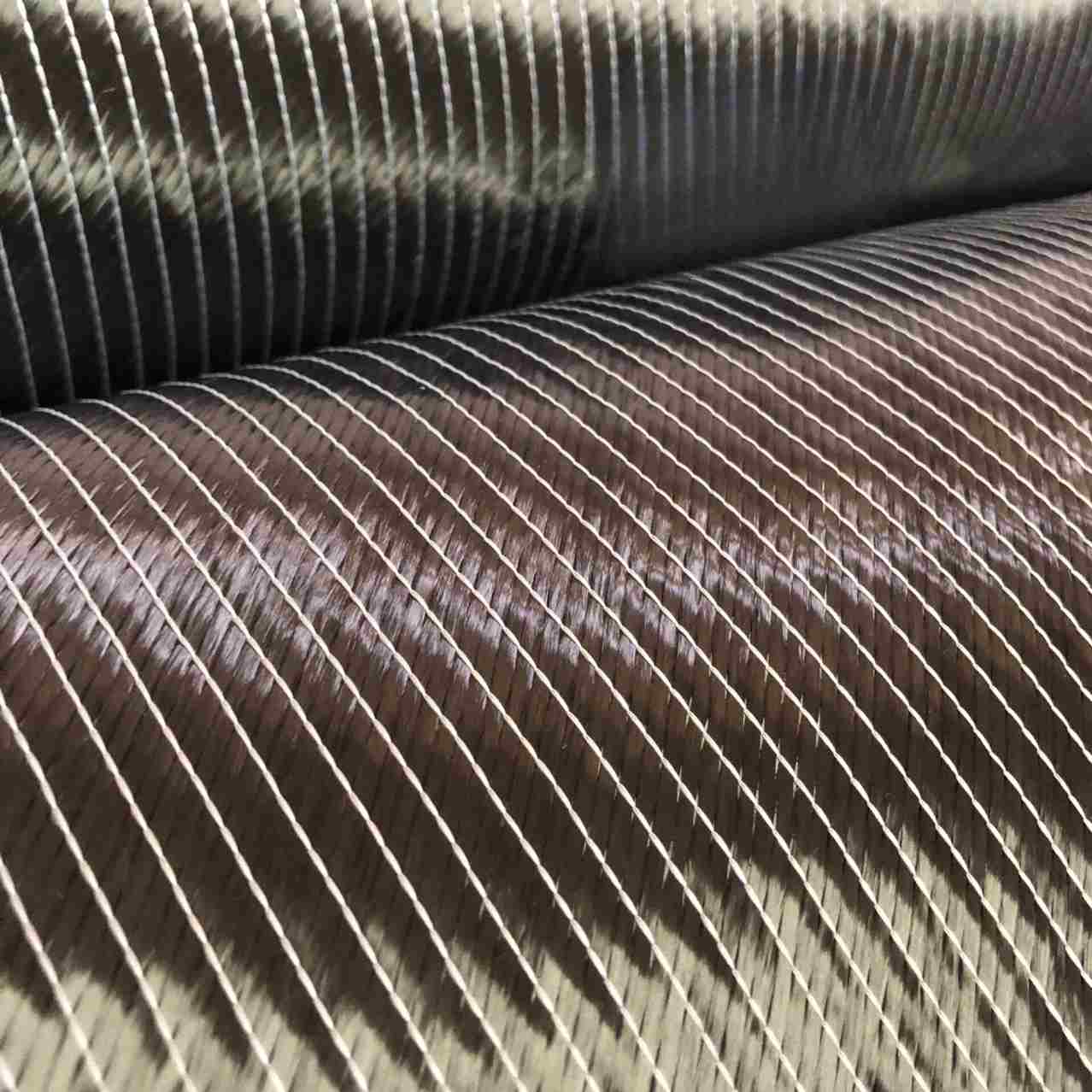
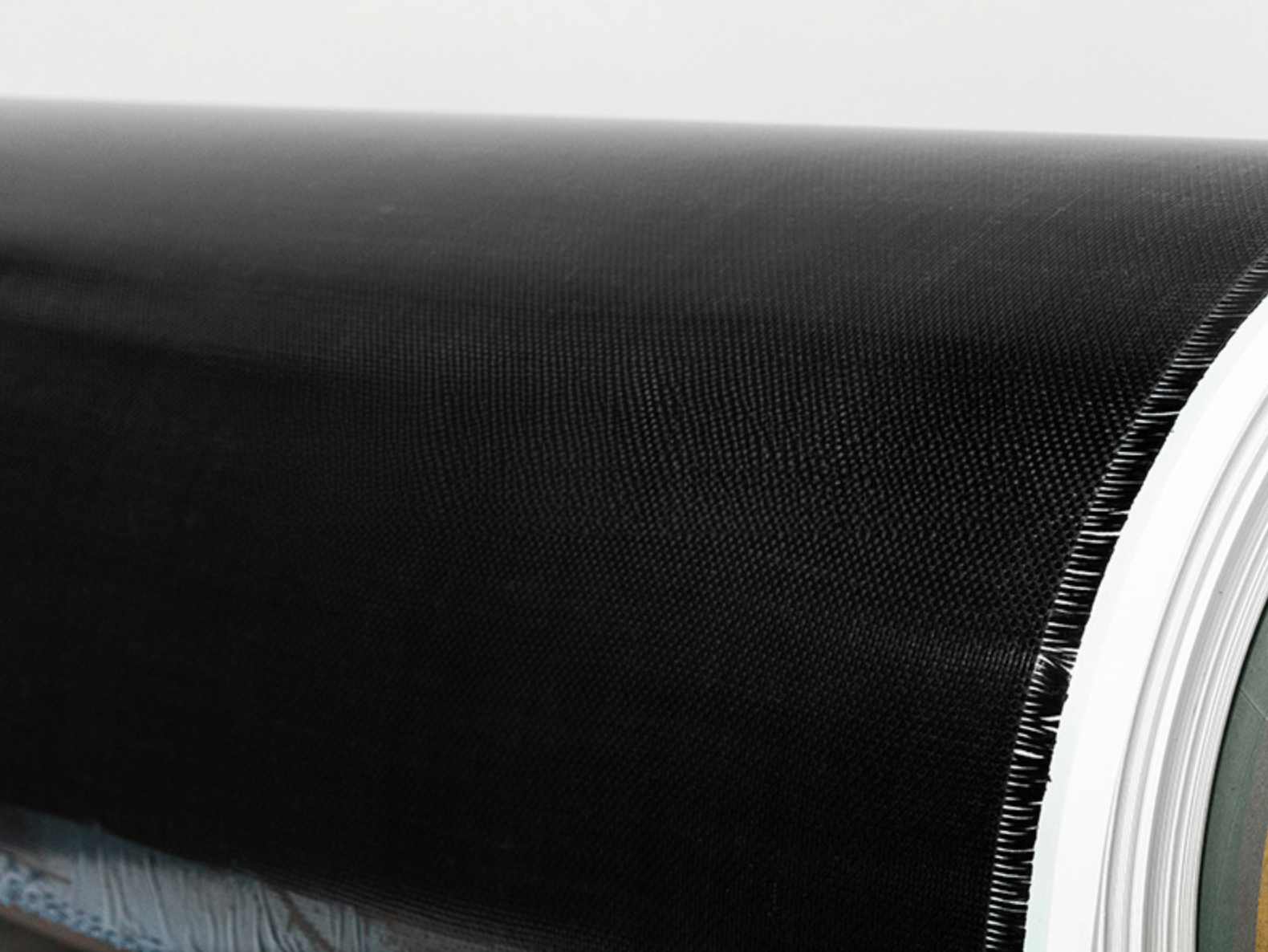
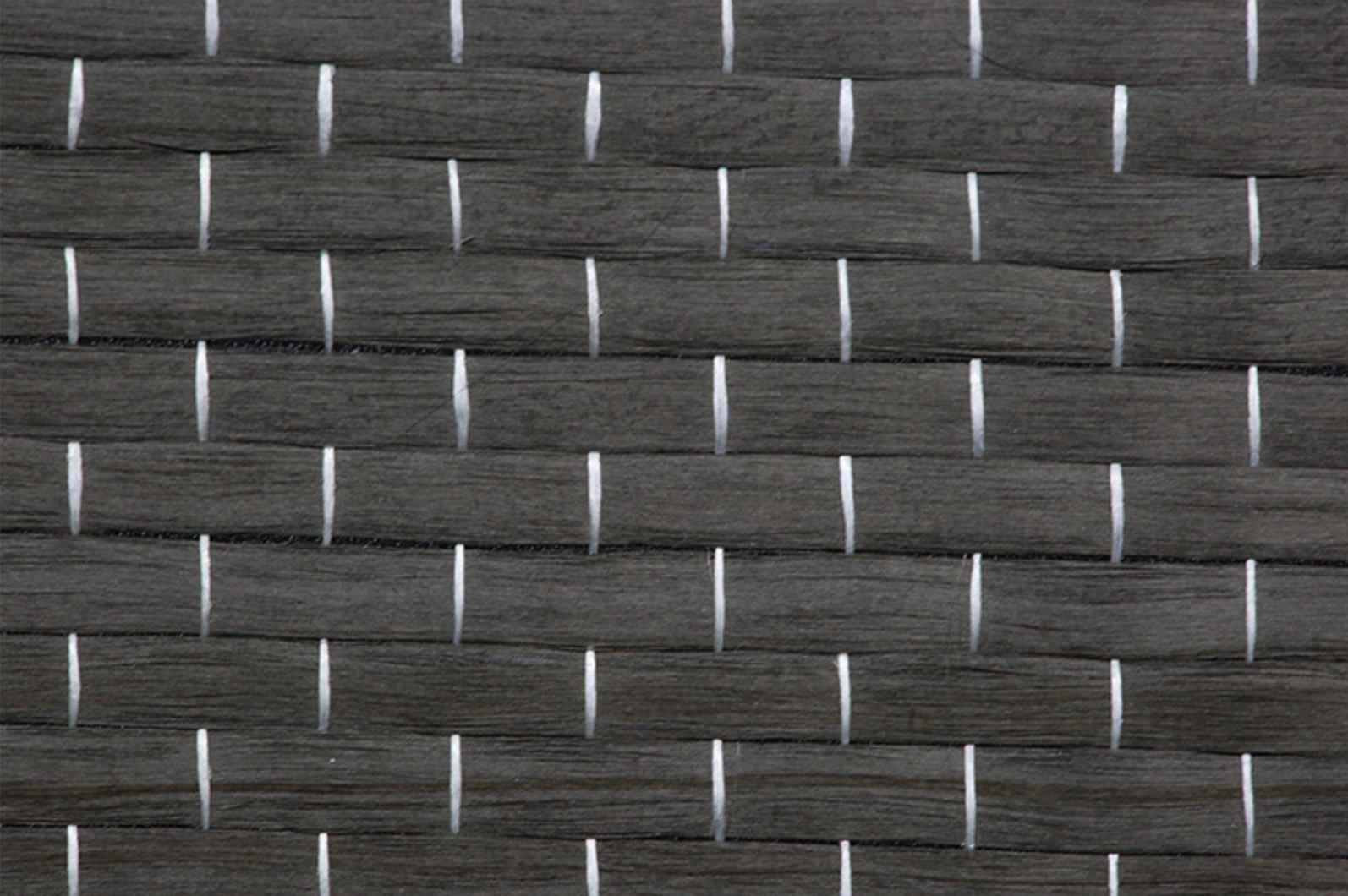
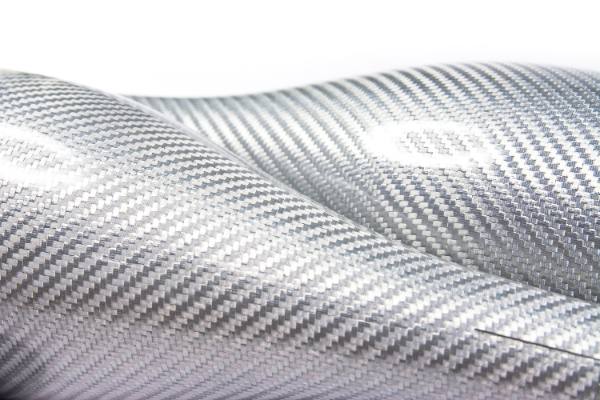
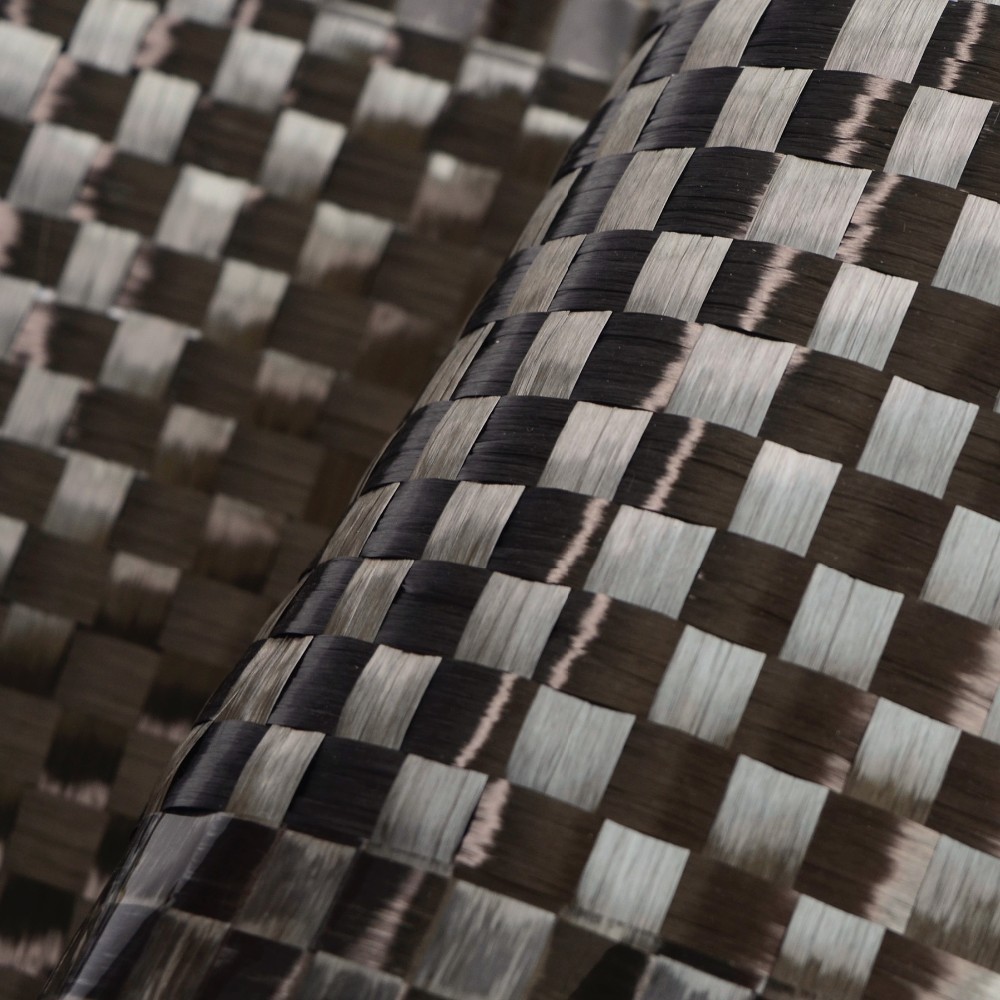
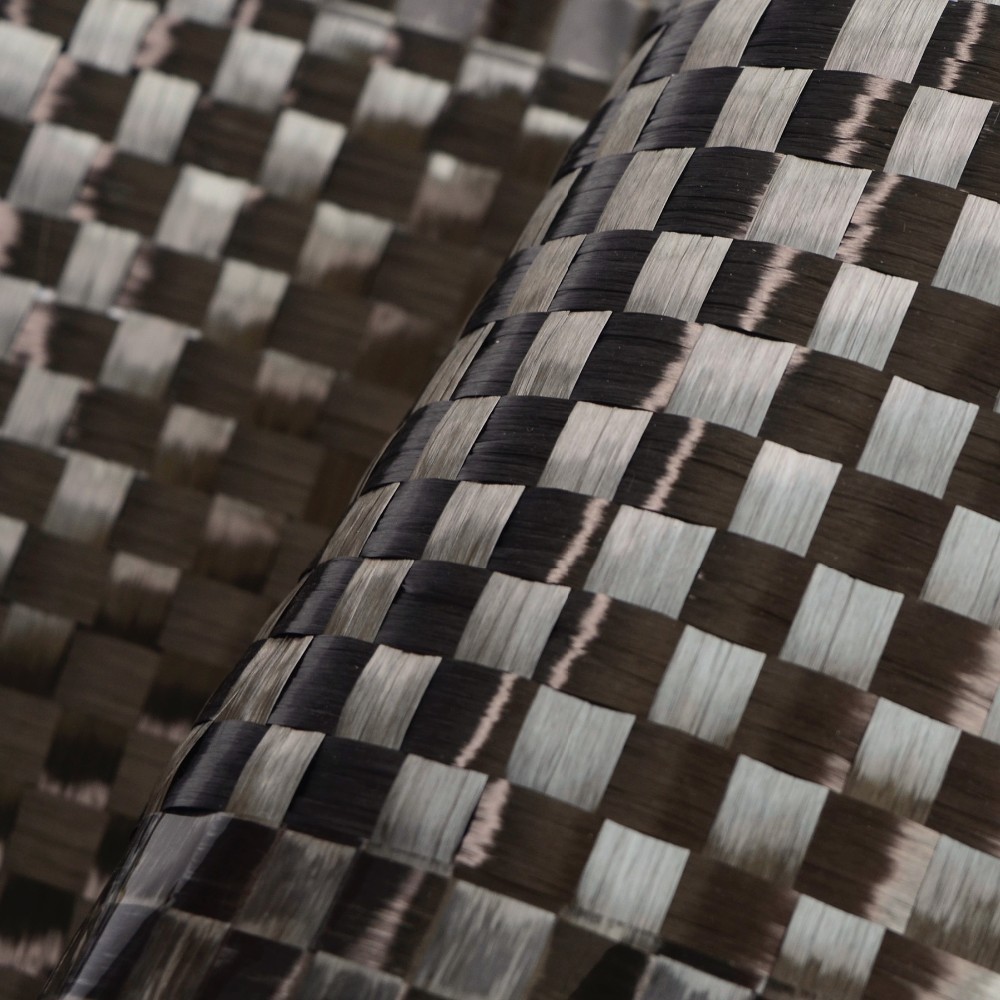
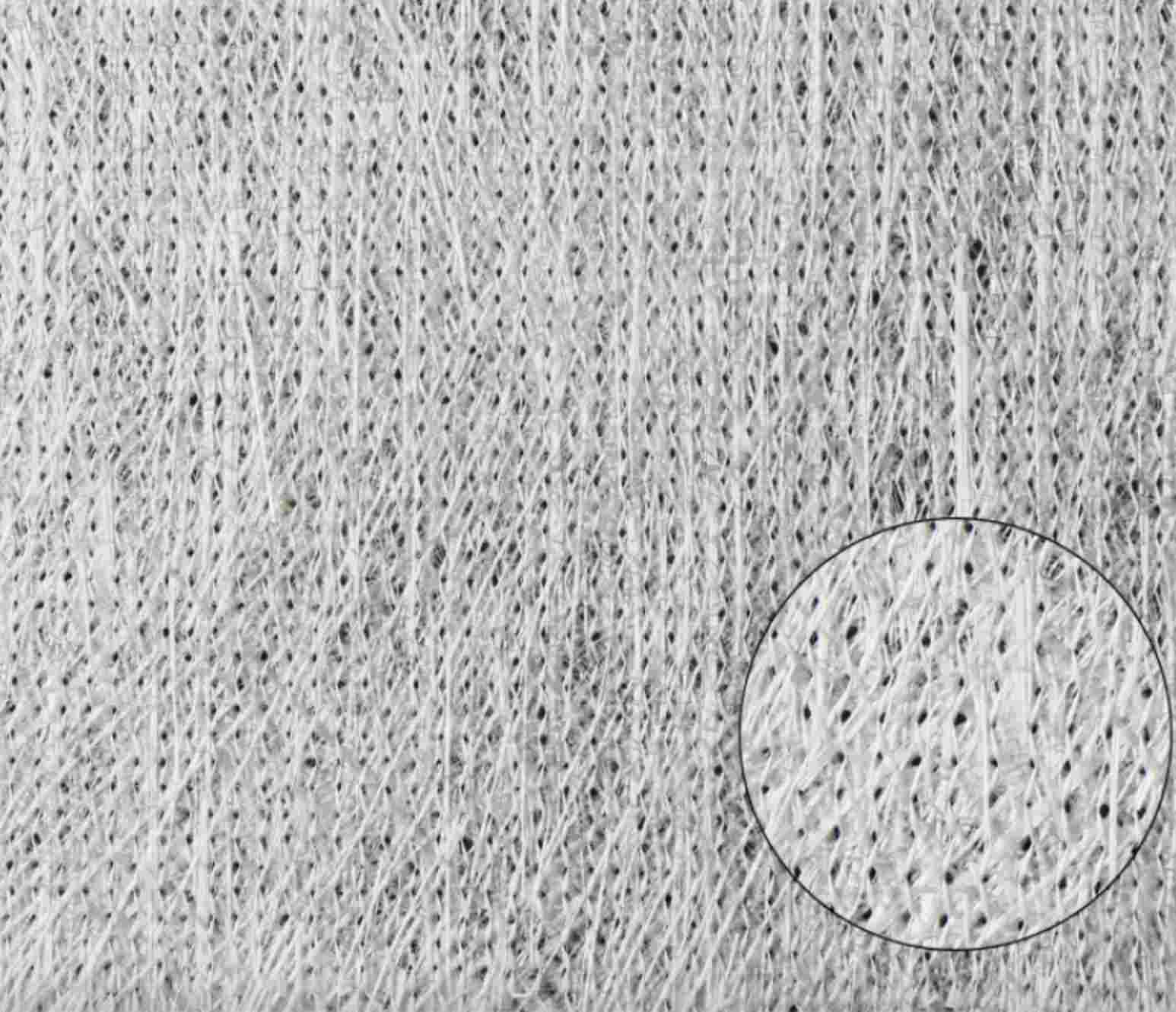
Fiberglass prepreg is a type of composite reinforcement material consisting of woven fiberglass fabric pre-impregnated with a resin system. The resin, usually an epoxy or other thermosetting polymer, is partially cured to a "B-stage" state, making it tacky but not fully hardened. This semi-cured state allows for easy handling and storage until final processing.
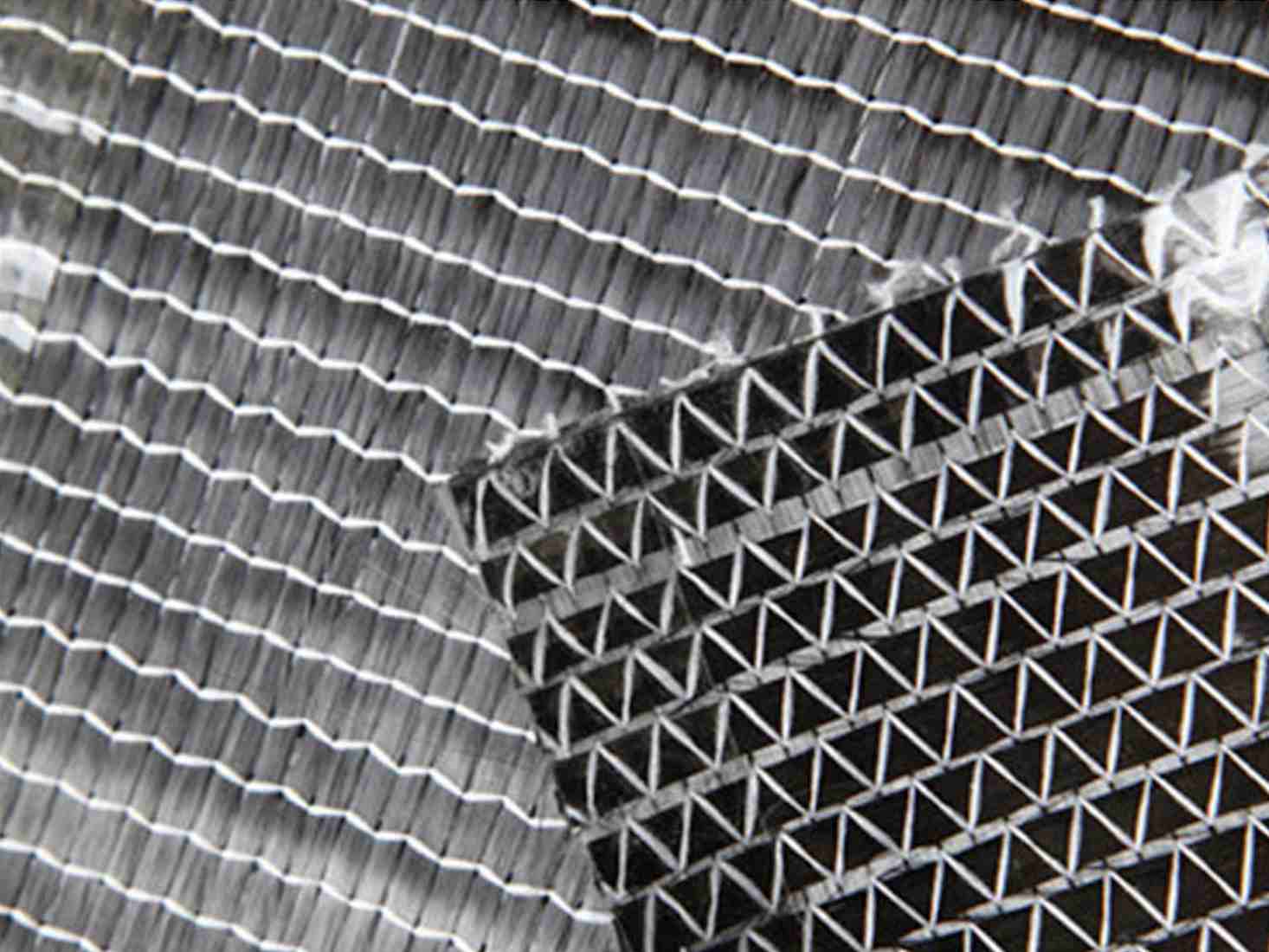
Types of Prepreg Fiberglass
There are various types of prepreg fiberglass, each with unique properties tailored to different applications:
1.Based on Fabric Weave:
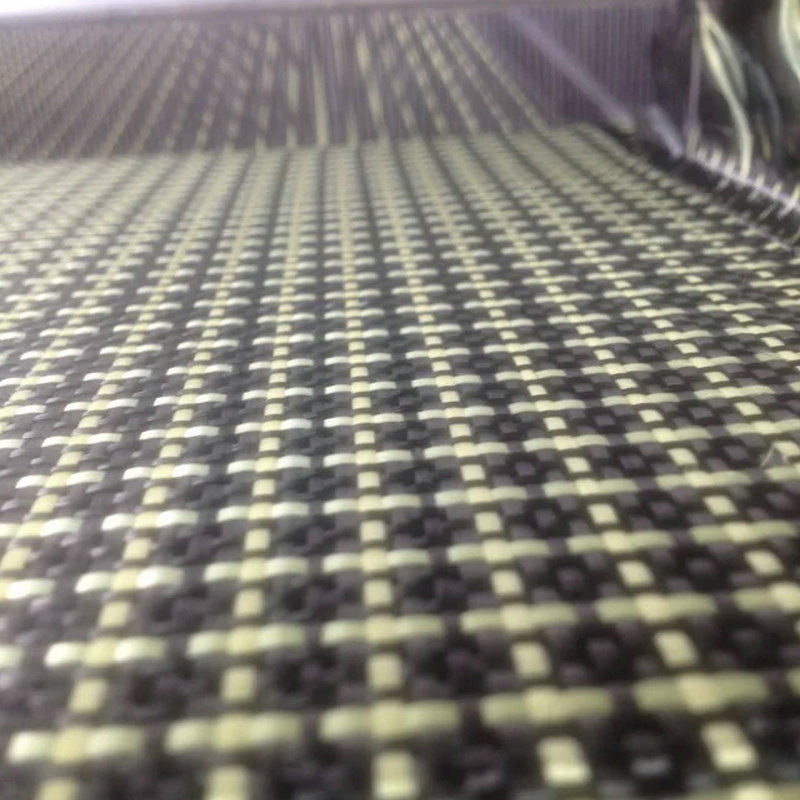
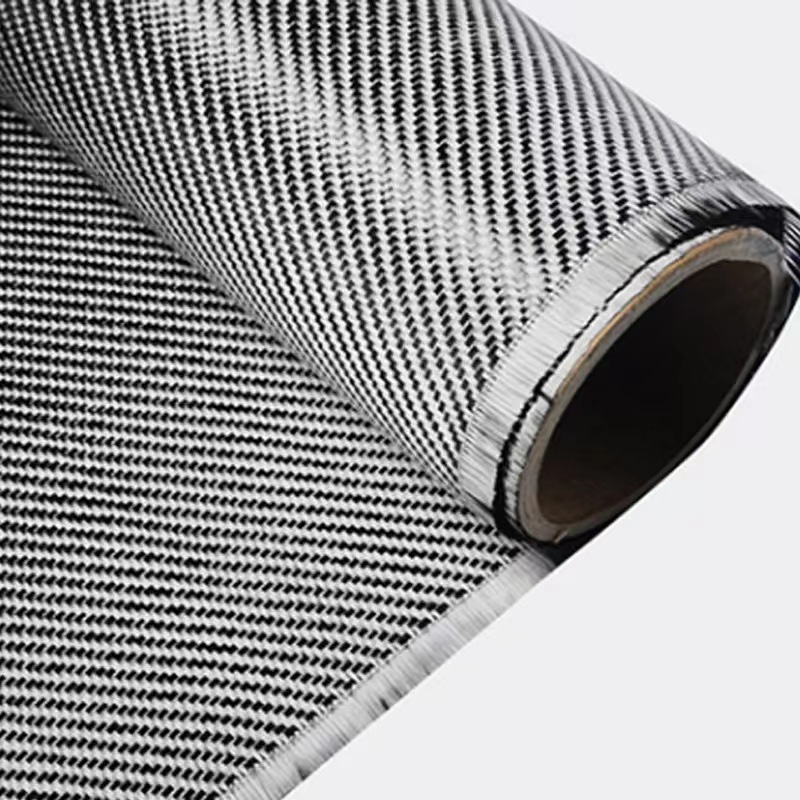
- Plain Weave: Offers a balanced combination of strength and flexibility.
- Twill Weave: Provides better drapability, making it ideal for complex curves.
- Satin Weave: Offers improved impact resistance and high strength.
- Unidirectional: Fibers are aligned in a single direction, maximizing strength along that axis.
2.Based on Resin Type:
- Epoxy Prepreg: The most common type, offering excellent mechanical and thermal properties.
- Phenolic Prepreg: Used in fire-resistant applications, especially in aerospace.
- Polyester/Vinyl Ester Prepreg: More cost-effective options for marine and general-purpose applications.
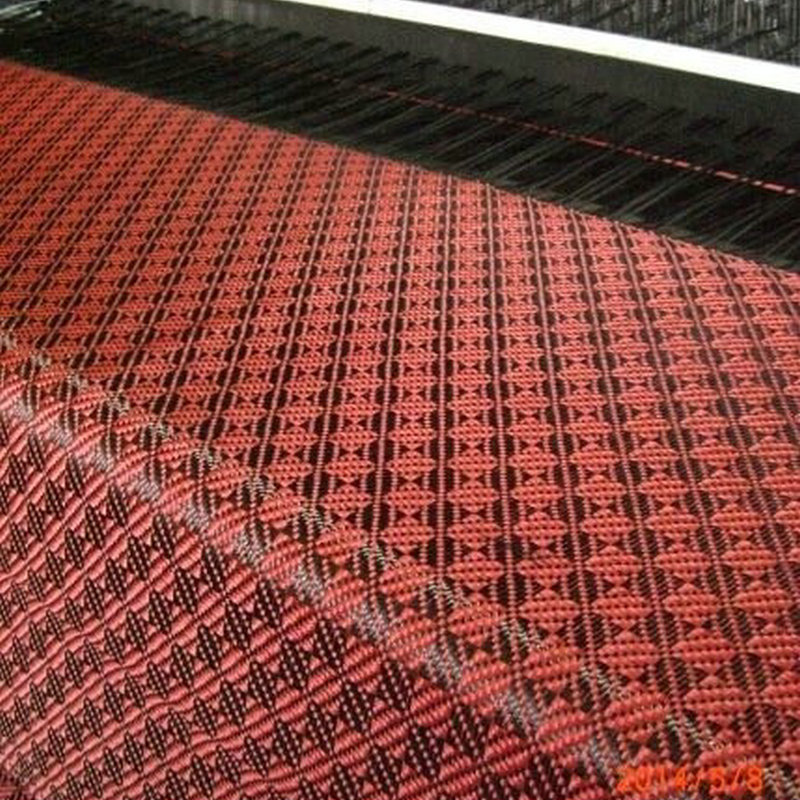
How is Fiberglass Prepreg Manufactured?
The production of fiberglass prepreg is a meticulous process that ensures uniform resin distribution and high-quality performance.
1. Selection of Fiberglass Fabric
Manufacturers choose fiberglass fabric based on the application’s strength, flexibility, and thermal resistance requirements. The fabric can be woven, non-woven, or unidirectional, depending on the intended use.
2. Resin Impregnation
The selected fiberglass fabric is fed through a resin impregnation machine where a thermosetting resin is applied under controlled conditions. The resin system typically includes curing agents and additives to enhance performance.
3. Partial Curing (B-Staging)
Once impregnated with resin, the material is partially cured (B-stage) to make it tacky but not fully hardened. This allows for easy handling, cutting, and storage without premature curing.
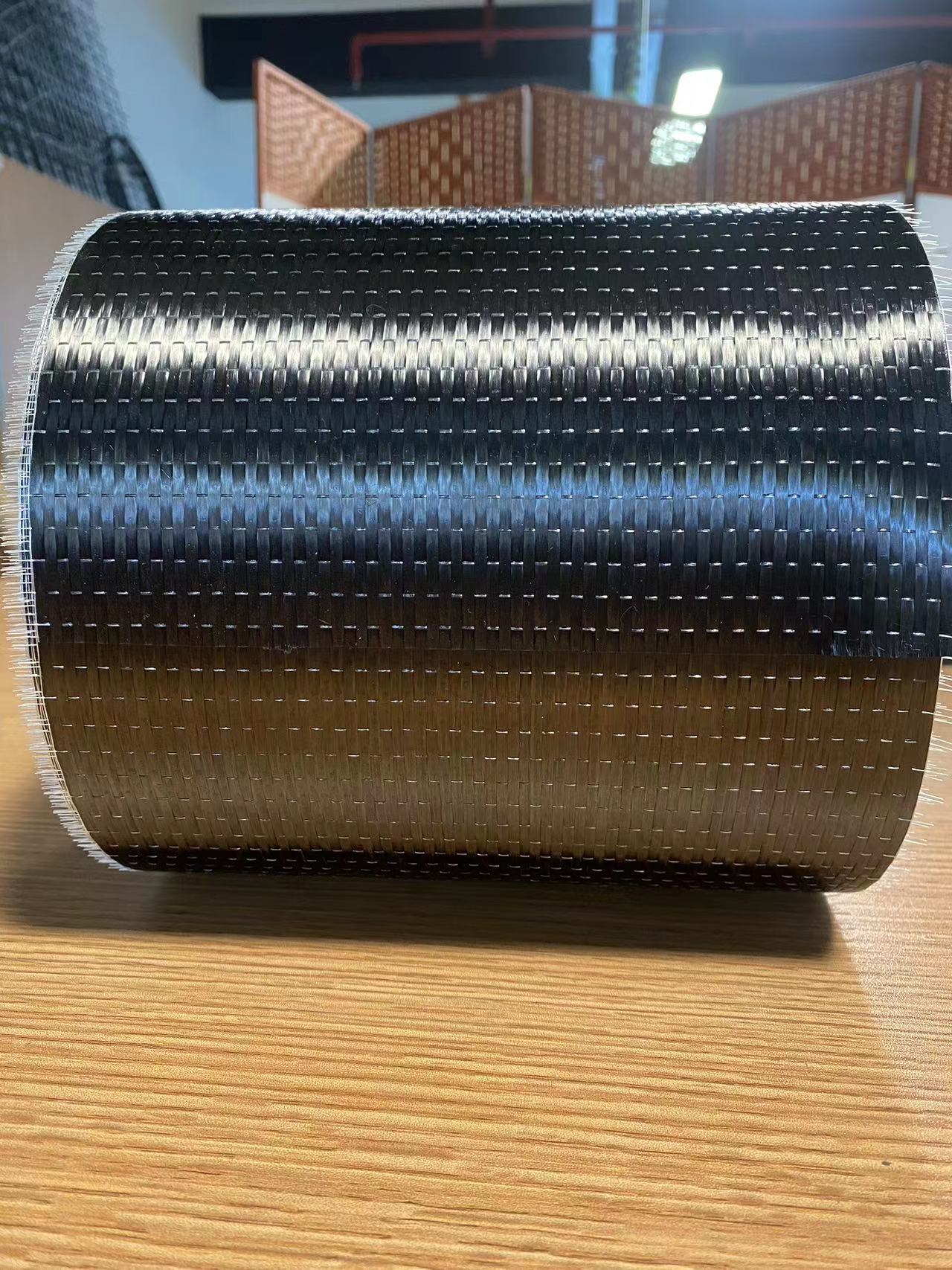
4. Quality Control and Packaging
The prepreg material undergoes strict quality control tests to ensure even resin distribution, proper fiber alignment, and mechanical integrity. It is then cut, rolled, and packaged for storage in a temperature-controlled environment.
Fiberglass cloth serves as the foundational reinforcement material in fiberglass prepreg, providing exceptional strength, flexibility, and durability for high-performance composite applications.
Advantages of Fiberglass Prepreg Over Traditional Fiberglass
1. Consistent Resin-to-Fiber Ratio
Unlike wet layup methods, where resin application can be inconsistent, fiberglass prepreg is manufactured with a precise resin-to-fiber ratio. This ensures optimal mechanical properties and reduces excess weight.
2. Enhanced Mechanical Properties
Prepreg fiberglass composites exhibit superior tensile strength, impact resistance, and fatigue durability. The controlled curing process results in fewer defects and better overall performance.
3. Reduced Material Waste
Since the resin is pre-applied, there is minimal excess material or spillage, reducing waste and cleanup time. This makes prepreg fiberglass a more efficient and environmentally friendly option.
4. Better Adhesion and Uniformity
The pre-impregnated resin system ensures uniform coverage across the fibers, reducing the risk of dry spots, air pockets, or inconsistencies that could compromise structural integrity.
5. Time and Labor Savings
Prepreg fiberglass eliminates the need for resin mixing and manual application, reducing production time and labor costs. This is particularly beneficial for high-volume manufacturing.
Applications of Fiberglass Prepreg in Different Industries
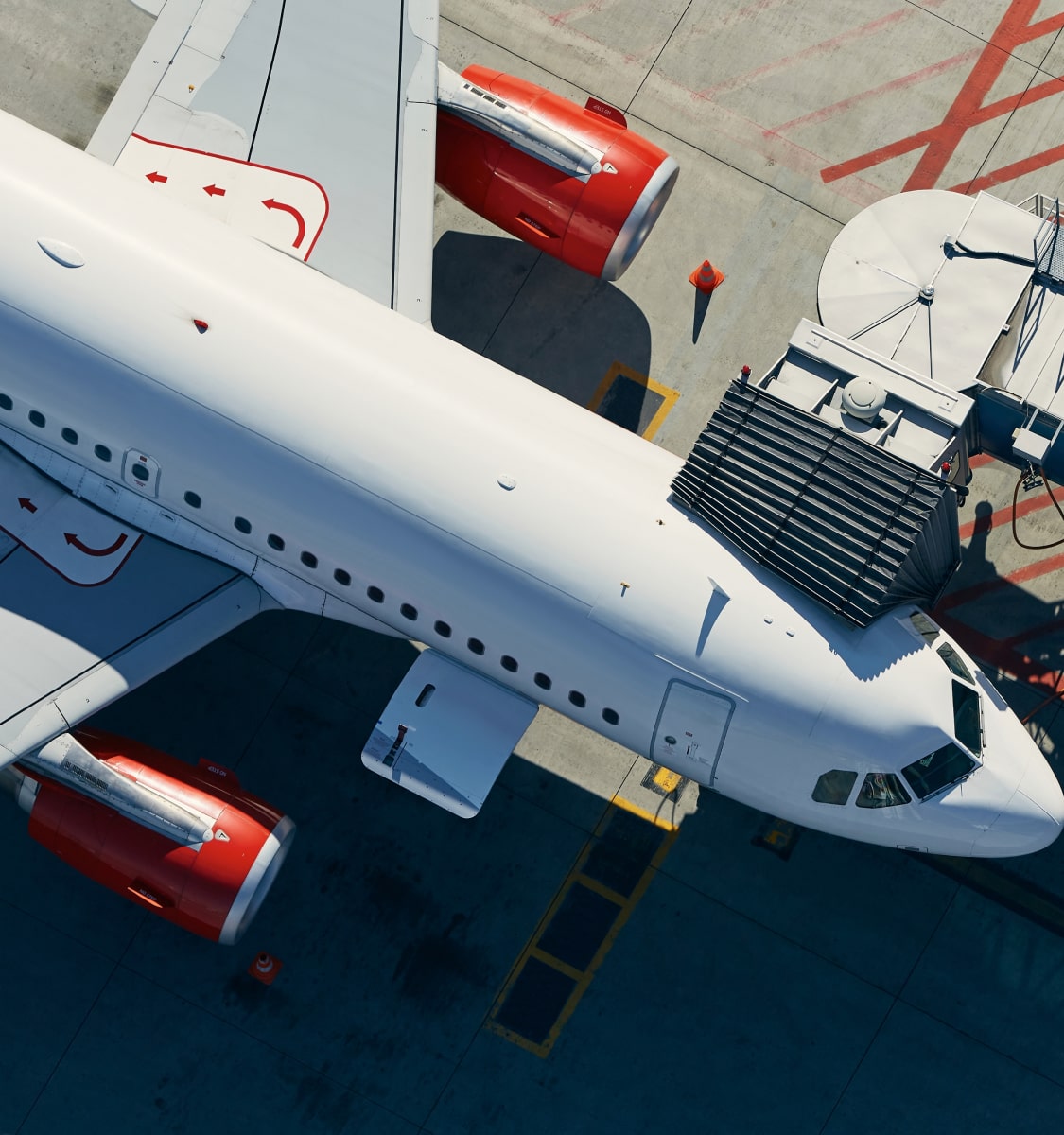
1. Aerospace and Aviation
Fiberglass prepreg is extensively used in aircraft fuselages, wings, and interior panels due to its lightweight yet strong properties. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical stress makes it ideal for aerospace applications.
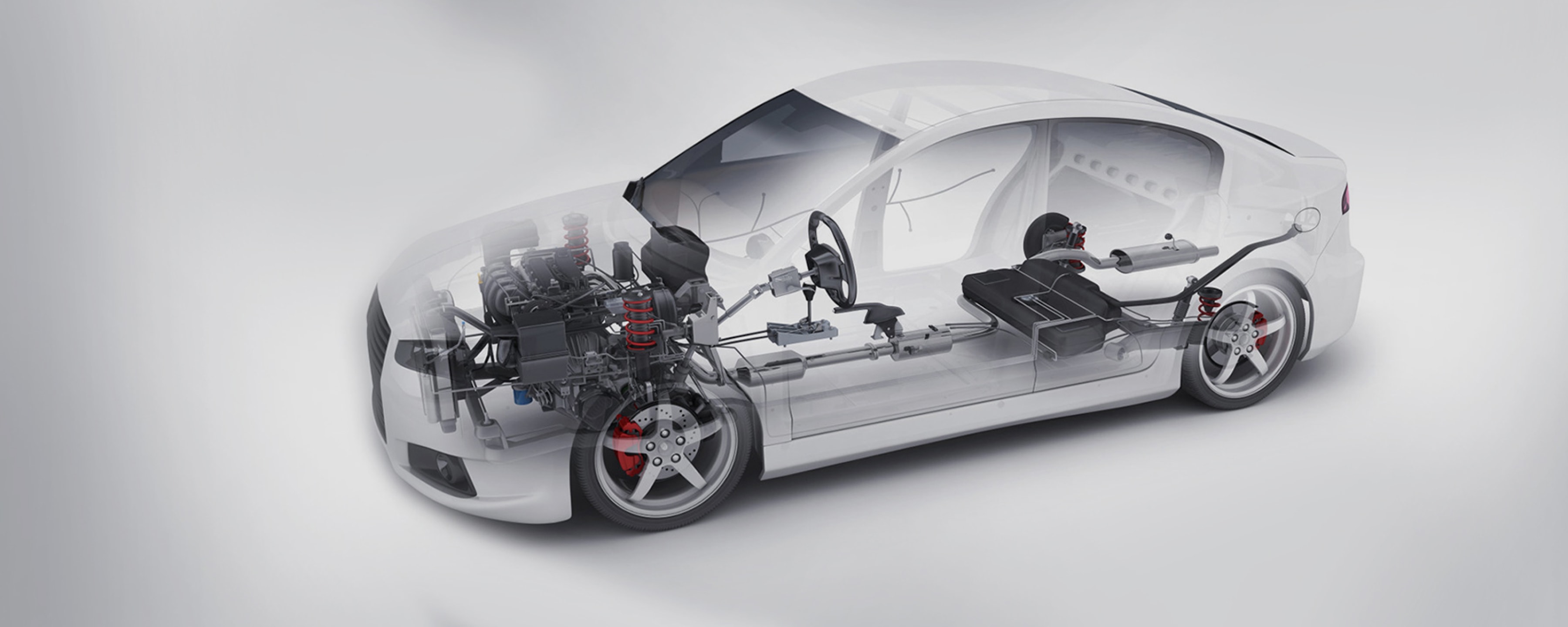
2. Automotive and Motorsports
High-performance and electric vehicles incorporate prepreg fiberglass in structural panels, chassis reinforcements, and aerodynamic components to enhance speed, fuel efficiency, and safety.
3. Marine and Boating
Boat manufacturers rely on fiberglass prepreg for hulls, decks, and masts because of its excellent corrosion resistance, water resistance, and durability in harsh marine environments.
4. Sporting Goods and Recreational Equipment
Bicycles, tennis rackets, golf clubs, and other sports equipment benefit from prepreg fiberglass’s lightweight and high-strength properties, enhancing performance and durability.
5. Industrial and Construction Applications
Prepreg fiberglass is used in industrial enclosures, wind turbine blades, and composite bridges, where high strength and environmental resistance are critical.
Processing and Curing Fiberglass Prepreg
1. Layup and Molding
Prepreg sheets are cut to specific shapes and layered onto a mold.
Vacuum bagging is used to remove air bubbles and ensure proper adhesion.
Layer stacking allows for customization of thickness and strength.
2. Curing Process
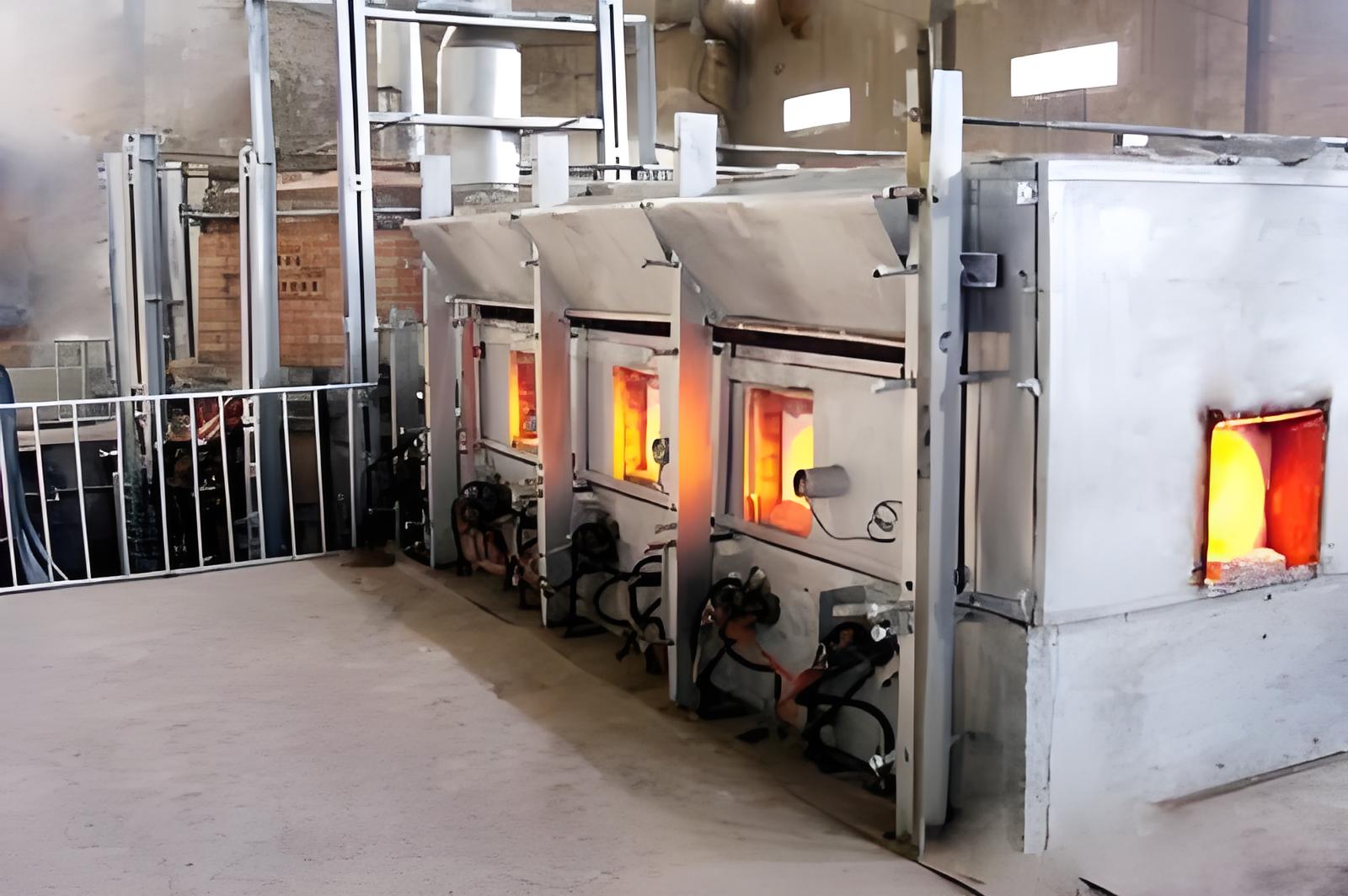
Curing requires heat and pressure to fully harden the resin and bond the fibers. The three main curing methods include:
- Autoclave Curing: Uses heat and pressure in a controlled chamber for high-quality results.
- Oven Curing: A cost-effective alternative that applies uniform heat for smaller projects.
- Press Curing: Utilizes heated platens to apply pressure and heat simultaneously.
Storage and Shelf Life Considerations
1. Refrigerated Storage
Fiberglass prepreg must be stored at temperatures below -18°C (0°F) to prevent premature curing. It should be thawed gradually before use.
2. Moisture Protection
Prepreg materials should be kept in moisture-proof packaging to prevent contamination and degradation.
3. Handling Guidelines
Use gloves to avoid contamination from oils and moisture.
Allow prepreg to reach room temperature before cutting or laying up.
Challenges and Limitations of Fiberglass Prepreg
1. High Cost
Prepreg fiberglass is more expensive than traditional fiberglass due to its controlled manufacturing process and resin formulation.
2. Specialized Storage Requirements
Requires refrigeration, which adds to logistics and handling complexity.
3. Processing Complexity
Curing fiberglass prepreg requires specific temperature and pressure conditions, necessitating specialized equipment like autoclaves or ovens.
Conclusion
Fiberglass prepreg has revolutionized composite materials by offering superior strength, precision, and performance. Its advantages over traditional fiberglass make it the preferred choice in aerospace, automotive, marine, and industrial applications. While the material requires specialized storage and processing, its benefits—such as uniform resin distribution, high mechanical strength, and reduced waste—make it a worthwhile investment.
As technology advances, we can expect further improvements in fiberglass prepreg materials, making them more accessible, sustainable, and cost-effective for future applications.
Read More: Preparation and properties of aramid 1414 needle-punched nonwoven filter material
Beliebte Verbundwerkstoffe
Beliebte Verbundwerkstoffe
Kompositeswissen Hub
Kompositeswissen Hub